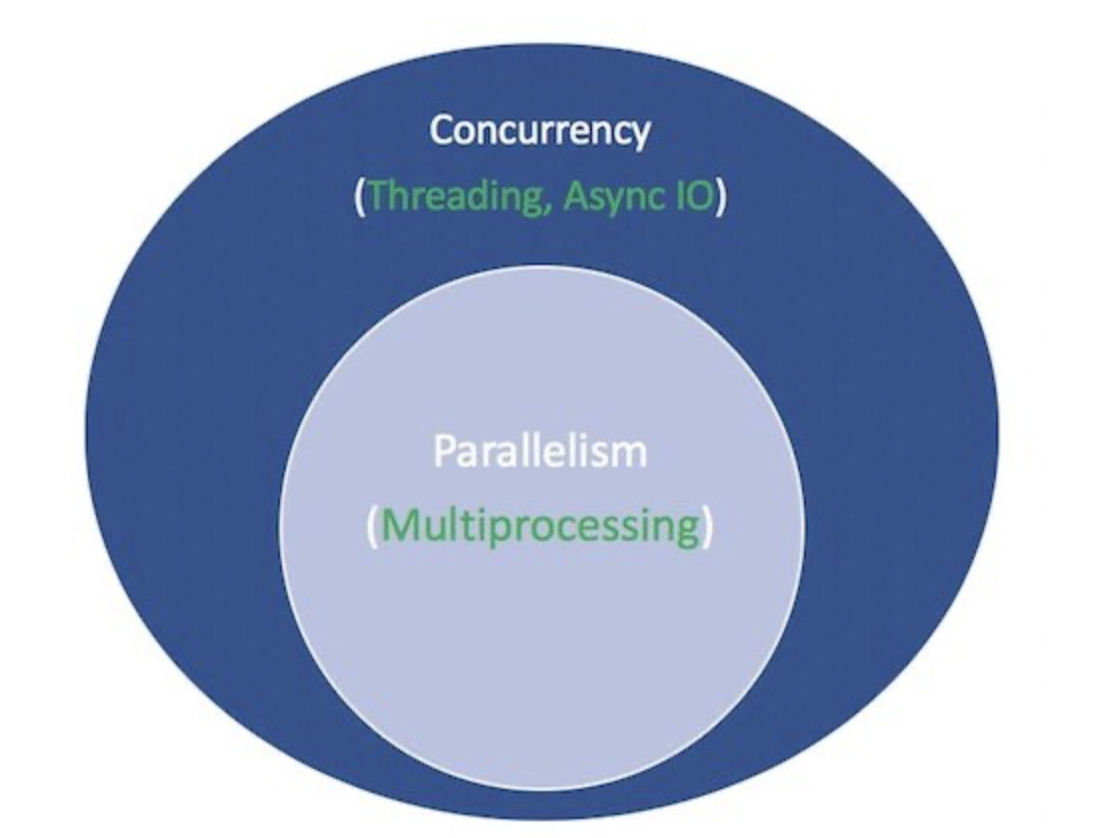
동시성과 4가지방법
동시성은 사실상 멀티프러세싱밖에 없음
스레딩과 비동기는 코드통제방식의 차이
스레딩은 운영체제가 맘대로 코드를 짤라내면서 자원 분배함. 결과적으로 속도개선.
비동기는 코드내에서 의미단위로 통제권 이양함.
동시성을 사용하는 이유
IO바운드와 CPU바운드 해결목적
입출력바운드 : 데이터 입출력이 느림.(파일시스템,네트워크). 비동기 프로그래밍이 해결책
CPU연산바운드 : 연산이 느림. 각 CPU마다 프러세스 하나씩 만들어주는 멀티프로세싱이 해결책. 프로세스>CPU이면 프로세스 이동시키는데 자원소모됨.
| I/O-Bound Process | CPU-Bound Process. |
| Your program spends most of its time talking to a slow device, like a network connection, a hard drive, or a printer | You program spends most of its time doing CPU operations |
| -> Speeding it up involves overlapping the times spent waiting for these devices | ->Speeding it up involves finding ways to do more computations in the same amount of time |
네가지 방법에 대해서 좀더 구체적인 설명(문제점/해결책/꿀팁)
1. Synchronous
The Problems With the Synchronous Version
: it’s relatively slow compared to the other solutions
그러나 코드실행주기가 길고, 속도가 비즈니스측면에서 ciritical하게 느리지 않다면 기본버전(동기화버전)만으로 충분한 해결책임.
2. Threading
The Problems with the threading Version
1) Because the operating system is in control of when your task gets interrupted and another task starts, any data that is shared between the threads needs to be protected, or thread-safe.
--> queue
--> threading lock
--> threading local
2) it takes a little more code to make this happen
: ThreadPoolExecutor, Executors
: create request.Session per thread!
3) Threads can interact in ways that are subtle and hard to detect. These interactions can cause race conditions that frequently result in random, intermittent bugs that can be quite difficult to find.
3.async
The lack of a nice wrapper. you have to do a little extra work to get much better performance.
[추가적인 설명]
4.multiprocessing
문제점 없음.. 헿
import multiprocessing
import time
def cpu_bound(number):
return sum(i * i for i in range(number))
def find_sums(numbers):
with multiprocessing.Pool() as pool:
pool.map(cpu_bound, numbers)
if __name__ == "__main__":
numbers = [5_000_000 + x for x in range(20)]
start_time = time.time()
find_sums(numbers)
duration = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Duration {duration} seconds")
| IO bound 기준으로 비교하기 | ||
| Threading | AsyncIO | Multi-processing |
#동시성 코드 사용법
1) 동시성 코드는 복잡하므로 웬만하면 피한다. deciding if you should use a concurrency module. concurrency always comes with extra complexity and can often result in bugs that are difficult to find.
2) 지연속도의 원인이 연산인지,입출력인지 확인한다. figuring out if your program is CPU-bound or I/O-bound is a great next step.
일반적인 해결가이드
1) CPU-bound problems : multiprocessing.
threading and asyncio did not help this type of problem at all.
2) I/O-bound problems, “Use asyncio when you can, threading when you must.” asyncio can provide the best speed up for this type of program, but sometimes you will require critical libraries that have not been ported to take advantage of asyncio.
Remember that any task that doesn’t give up control to the event loop will block all of the other tasks. 이벤트 루프 제어권 가진 모든 task는 블록킹을 한다.
GIL 은 동시성을 어떻게 제어하니?
GIL은 CPU바운드를 걸어놓는 락 장치다. GIL땜에 멀티스레딩해도 바운드문제가 해결되지 않음.
https://realpython.com/python-gil/
* GIL에 대한 기술적 상세설명은 POSIX THREAD 글 읽기
https://realpython.com/python-concurrency/
'Developing.. > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 로그남기는 법 : Logging wrapper만들기 (0) | 2022.07.09 |
|---|---|
| python --config ..설정값 관리하기! (0) | 2022.06.09 |
| Socket Programming w/ Multithreading (0) | 2021.02.09 |
| Projects in Python - price notifications (0) | 2021.02.05 |
| Testing in Python (0) | 2021.02.05 |